Abstract
Introduction: Mutations (MT) in the 5' untranslated region (UTR) of ANKRD26 (A26) are implicated in A26-related thrombocytopenia (A26 RT), an autosomal dominant disorder of mild to moderate thrombocytopenia (TP), usually presenting in adulthood. Germline (GL) MT in A26, ETV6, and RUNX1 constitute a category of myeloid neoplasms (MN) with GL predisposition and preexisting platelet (plt) disorders per 2016 WHO criteria. While this TP is not life-threatening, ~10% of patients (pts) develop a MN. UTR variants (vars) are well described. However, A26 coding vars (A26 CV) are also reported to segregate with familial TP. Despite this, some studies and diagnostic tests are limited to the 5'UTR; as such, A26 CV are not well described or linked to MN.
Methods: Whole exome sequencing (WES) data from 5,561 MN pts from various institutions was subjected to standard pipelines for rare GL variant discovery. After applying stringent filtering criteria to nonsynonymous exonic A26 CV, including population frequency (PF) <0.001 and predicted pathogenicity by at least 5/6 structure prediction algorithms, we identified 31 A26 CV in 56 pts (1%). Vars not meeting this criteria (n=91) were classified as SNPs.
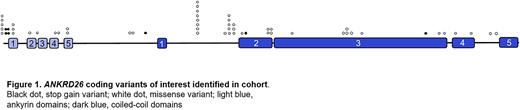
Results: There were 25 missense and 6 stop gain vars (Figure 1); 3 occurred in ankyrin and 14 in coiled-coil domains, both of which interact with signaling and cytoskeletal proteins. The median (med) PF was 8.3x10-6 (range (ran) 0-9.0x10-4) with med VAF of 47% (ran 5-100%). Two vars, p.E1526K (VAF 5%) and p.K473X (VAF 23%) likely represented somatic origin, and were not further considered; another 2, p.M1I and p.Y35X, were reported in familial TP. Confirmation of GL status was available for 2 vars, p.D656V and p.T82M. Sub cohort analysis of 4,376 pts revealed 125 (2.8%) with more than one var: 1 with 2 A26 CV, 8 with 1 A26 CV and 1 SNP, 3 with 3 SNPs and 113 with 2 SNPs.
Clinical data was available for 12 A26 CV pts. Pts were diagnosed at med age of 75 (ran 61-84) with MDS (n=7), AML (n=2), and CMML (n=3). Cytogenetics were normal, except two pts had trisomy 8. Med plt count was 191 k/μL (ran 17-472), however 5 pts had plt count below 150 k/μL, 3 of whom harbored the p.D656V var (PF 3.5x10-5). Another pt, whose plt count was 160 k/μL, also had the p.D656V var. Additional sequencing was examined in 2/12 pts and revealed one pt with RUNX1 p.R162G, and the other with SETBP1 p.D814N, KRAS p.I136M, and MED12 p.R961W, suggesting that multiple MT are implicated in overt MN.
Some pts with A26 CV had a giant plt phenotype, prompting further examination for 567 genes implicated in plt disorders and biogenesis. Vars in both the dynein (DYN) and kinesin (KIN) family of genes (DNAH14 p.1923_1924del, KIF23 p.A290S; DNAH2 p.A2489T, KIF26 p.T769M) were associated with giant plts. In sub cohort analysis of 1017 MN pts with WES, we identified 4 pts with 2 DYN vars each, 1 pt with 2 KIN vars, 12 pts with 1 DYN var, 3 pts with 1 KIN var, 1 pt with 3 KIN vars, and 7 pts with DYN and KIN vars (of whom 2 harbored A26 SNPs). In 11 pts (70%) with DYN vars, giant plt were observed vs. 40% (n=2) of those with KIN and 86% (n=6) with both DYN and KIN. This suggests a synergistic role between proplatelet elongation (DYN) and alpha-granule secretion (KIN) in the formation of giant plt.
Analysis for 5' UTR vars was available for 4,376 pts and identified c.-113A>C (n=2; PF 1.9x10-4) and c.-140C>G (n=434; PF 6.4x10-2), both found in A26 RT (canonical), as well as c.-147T>G (n=1; PF 0), c.-154C>T (n=2; PF 3.x10-5), and c.-59G>A (n=381; PF 7.7x10-2), unreported in A26 RT (non-canonical). There were 19 pts with both canonical and non-canonical 5' UTR vars, 2 pts with canonical and A26 CV and 3 pts with non-canonical and A26 CV. The presence of a 5'UTR var was not associated with a greater degree of TP or higher BM blast percentage.
Conclusion: In a large cohort of MN, we report several novel findings: A26 CV are found in familial TP and MN; A26 SNPs, in various multi-hit configurations as well as in conjunction with DYN/KIN also occur in MN; and finally, the presence of non-canonical A26 5'UTR in MN. The role of A26 in predisposition to MN is not limited to canonical 5'UTR vars.
Disclosures
Mukherjee:AbbVie: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Advisor or review panel participant; Blueprint Medicines: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Advisor or review panel participant; Celgene/Acceleron: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Advisor or review panel participant, Research Funding; Genentech: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Aplastic Anemia and MDS International Foundation: Honoraria; BMS: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Advisor or review panel participant, Research Funding; Novartis: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Advisor or review panel participant, Research Funding; McGraw Hill Hematology Oncology Board Review: Honoraria, Other: Advisor or review panel participant; Partnership for Health Analytic Research, LLC: Honoraria; BioPharm: Consultancy; Jazz Pharmaceuticals: Other: Principal investigator for Investigator Initiated Trials (the Institution gets the funding), Research Funding; Eusa Pharma: Consultancy, Other: Advisor or review panel participant; Teaching and Speaking. Advani:Amgen: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Pfizer: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Immunogen: Research Funding; Kite: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; OBI: Research Funding. Gerds:Accurate Pharmaceuticals: Research Funding; Incyte Corporation: Research Funding; Bristol Myers Squibb/Celgene: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Kratos Pharmaceuticals: Research Funding; CTI BioPharma: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Novartis: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Imago BioSciences: Research Funding; AbbVie: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Sierra Oncology: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Morphosys/Constellation: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; PharmaEssentia: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Saunthararajah:EpiDestiny: Consultancy, Current equity holder in private company, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Patents & Royalties: intellectual property with royalty rights ; Novo Nordisk: Consultancy. Carraway:AbbVie: Other: DSMB; Takeda: Other: DSMB; Stemline: Speakers Bureau; Syndax: Other: DSMB; Novartis: Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Gilead: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Jazz: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; CTI Biopharma: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; BMS: Consultancy, Honoraria, Speakers Bureau. Nadarajah:MLL Munich Leukemia Laboratory: Current Employment. Meggendorfer:MLL Munich Leukemia Laboratory: Current Employment. Maciejewski:Apellis Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy; Alexion: Consultancy. Patel:Apellis Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy, Other: Teaching and Speaking; Alexion: Consultancy, Other: Teaching and Speaking; Novartis Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal